Ethereum Ultrasound Money: What is and how this MEME came up!

Ethan Nelson
November 28, 2022
10 min read

The concept of "ultrasound money" within the Ethereum community not only showcases the blend of technology and meme culture but also represents a pivotal shift in how value and scarcity are perceived in the blockchain ecosystem. This comprehensive exploration aims to dissect the multifaceted narrative of Ethereum's evolution into what many enthusiasts refer to as "ultrasound money," emphasizing its implications for staking enthusiasts and the broader crypto market.
What is Ethereum Ultrasound Money
Ultrasound money is a term that has surged in popularity within the Ethereum community, symbolizing a new era for the blockchain's economy post the ETH merge. Unlike traditional or even digital money, ultrasound money embodies the principles of absolute scarcity, deflationary mechanisms, and robust security, all thanks to Ethereum's transition to proof-of-stake (PoS) and the introduction of mechanisms like ETH burn. This evolution positions Ethereum as not just a platform for dApps and smart contracts but as a foundational layer for a new kind of money, one that aims to be more sound than even "sound money" like Bitcoin.
Basically, Ethereum Ultrasound Money refers to the concept of Ethereum achieving the status of sound money, a term popularized by the cryptocurrency community to describe a form of currency that holds its value over time, is resistant to manipulation, and serves as a reliable store of wealth. The term "ultrasound" emphasizes the idea of Ethereum continually striving to maintain a sound monetary policy.
What is the Origin of the MEME Ultrasound Money?
The MEME "ultrasound money" began circulating within the Ethereum community as a playful but pointed critique of Bitcoin's designation as "sound money." The term gained traction, especially around the discussions of the ETH merge, highlighting Ethereum's potential to surpass Bitcoin's economic assurances by reducing its issuance rate and introducing a burn mechanism via EIP-1559. This burn mechanism, colloquially known as "watch the burn," systematically destroys a portion of the ETH gas fees, potentially leading to a net reduction in Ethereum's supply over time—hence, the ultrasound.
Understanding the Ethereum Ultrasound Money Narrative
The narrative of Ethereum as ultrasound money is deeply intertwined with its economic and technological upgrades, particularly the ETH merge and EIP-1559. These developments not only improve Ethereum's scalability and efficiency but also its monetary policy. The ultrasound money narrative is compelling for staking enthusiasts and investors, as it promises a blockchain that's not just a platform for applications but also a robust store of value that can rival, if not surpass, traditional sound money principles.
How Ethereum Aims to Achieve Ultrasound Money Properties
Ethereum's journey towards becoming ultrasound money is paved with significant upgrades like the transition to PoS and the implementation of fee-burning mechanisms. By significantly reducing energy consumption through the ETH merge, Ethereum becomes more sustainable and scalable. Simultaneously, the ETH burn mechanism introduced in EIP-1559 makes Ethereum's supply deflationary under certain network conditions. These steps are critical in achieving the properties of ultrasound money: scarcity, security, and sustainability.
- Scarcity and Predictability: From Ethereum's perspective, achieving Ultrasound Money status involves promoting scarcity, predictability, and decentralization within its ecosystem.
- Alignment with Sound Money Principles: Ethereum seeks to align its protocol, governance, and economic incentives with the principles of sound money to enhance its credibility and utility as a digital currency.
A glimpse of tokenomics
The tokenomics of Ethereum, especially post-merge, focuses on creating a deflationary pressure on the supply of ether. This is achieved through the combination of reduced block rewards for validators and the burning of a portion of transaction fees. This deflationary model is a key aspect of what makes Ethereum ultrasound money, as it introduces a novel economic model that could theoretically lead to a decrease in total supply over time, assuming the network's use and the amount of ETH burned outpace the issuance.
An overview of crypto supply
In the broader context of crypto supply, Ethereum's approach to managing its supply is groundbreaking. Most cryptocurrencies have a predetermined issuance schedule, but Ethereum's move to burn transaction fees introduces a dynamic mechanism that adjusts supply based on network activity. This is in stark contrast to cryptocurrencies with fixed supply caps or linear issuance, positioning Ethereum uniquely in the crypto supply discussion.
The Tokenomics of Minting and Burning
Minting and burning are two sides of the cryptocurrency supply coin. While minting introduces new tokens into circulation, burning removes tokens permanently from the supply. Ethereum's economic model now incorporates both, with new ether being minted as rewards for validators and a portion of transaction fees being burned. This dual approach balances the need for incentivizing network security with the desire to create a deflationary supply dynamic.
Let's return to Economics 101 to help us better understand Ultrasound money.
The basics of supply and demand tell us that when supply decreases, value increases, and vice versa. Simply put, the more rare an asset is, the more it will cost. Furthermore, since the supply of gold is steady and demand for it increases over time it’s value should always increase. Fast forward to the wild west of tokenomics, and we’re willy-nilly manipulation of supply and demand. We're minting tokens out of thin air, and the value of each token is volatile as a result.
Ethereum's Issuance, Burn Rate, and Supply Economics
In order to fully understand Ultrasound Money we need to touch on issuance and burn rates. Issuance and burning are quite simple concepts. Issuance refers to the amount of a token that are minted, while burn refers to the amount that is taken out of the total supply. Based on supply and demand logic, it’s better for a token to have a higher burn rate than issuance rate so that the value of the token increases with time.
Now you may be asking what the point of minting Ether out of thin air may be. Why is it something that blockchains do in the first place? Wouldn't this dilute the supply and decrease the price of Ethereum? The answer is pretty simple. Validating transactions is at the core of blockchain's innovation. With Proof of Work, miners are rewarded with Ethereum every time they complete a complex algorithm to secure the block. This reward comes from Issuance. In short, the supply is diluted to a minuscule level to ensure the security of the blockchain.
Post merge Ethereum’s burn rate will surpass its issuance rate. This decreasing supply of Ethereum over time is made possible because staking validator rewards aren’t as expensive for the network as PoW mining rewards. Thus, the amount issued (think issuance) to validators is lower than the amount Ethereum is burning.
As it currently stands with Ethereum's Proof of Work consensus mechanism, the issuance rate is roughly 13,500ETH/day. In other words, Ethereum's security mechanism rewarded validators with a fraction of the 13,500ETH minted out of thin air daily in exchange for their contribution to the network.
Since the merge, the Issuance rate has decreased to 1,600ETH/day, which is an 8x reduction in Issuance. Triple Halvening refers to this 8x reduction because if you cut 13,500 in half three times, you get the new PoS Issuance rate.
On top of that, the burn rate for PoS will be ~5,000ETH/day, meaning that the total supply of Ether in the market will decrease by roughly 3,500 ETH/day.=
What is the Ethereum perspective to become ultrasound money?
From the Ethereum perspective, becoming Ultrasound Money entails implementing mechanisms that promote scarcity, predictability, and decentralization. This involves optimizing Ethereum's protocol, governance, and economic incentives to align with the principles of sound money.
What is a sound money?
Sound money refers to a form of currency that maintains its value over time, possesses intrinsic qualities like scarcity and fungibility, and is resistant to inflationary pressures and manipulation. Bitcoin is often hailed as the quintessential example of sound money due to its limited supply and decentralized nature.
- Sound Money Bitcoin's Example: Bitcoin serves as the quintessential example of sound money, characterized by its capped supply of 21 million coins and decentralized nature.
How Bitcoin Created Sound Money
Bitcoin introduced the concept of sound money to the digital realm by implementing a hard cap on its total supply at 21 million coins, mimicking the scarcity and durability of precious metals. This cap, combined with a decentralized network secured by miners, established Bitcoin as a viable digital counterpart to traditional sound money concepts. Bitcoin's model of reducing new supply over time through halving events further cemented its status, creating a predictable deflationary currency that contrasts with the inflationary nature of fiat currencies.
- Limited Supply: Bitcoin's creation with a fixed supply and deflationary issuance schedule laid the foundation for sound money principles within the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Sound Money vs. Ultrasound Money: A Tale of Two Properties
While Bitcoin is celebrated as digital sound money, Ethereum's evolution proposes a new paradigm: ultrasound money. The distinction lies in Ethereum's dynamic supply mechanism, which, unlike Bitcoin's fixed supply, can potentially become deflationary through the burning of transaction fees. This mechanism suggests that Ethereum could not only maintain but increase its purchasing power over time, outpacing the sound money characteristics of a fixed supply by adapting to network demands and activity levels.
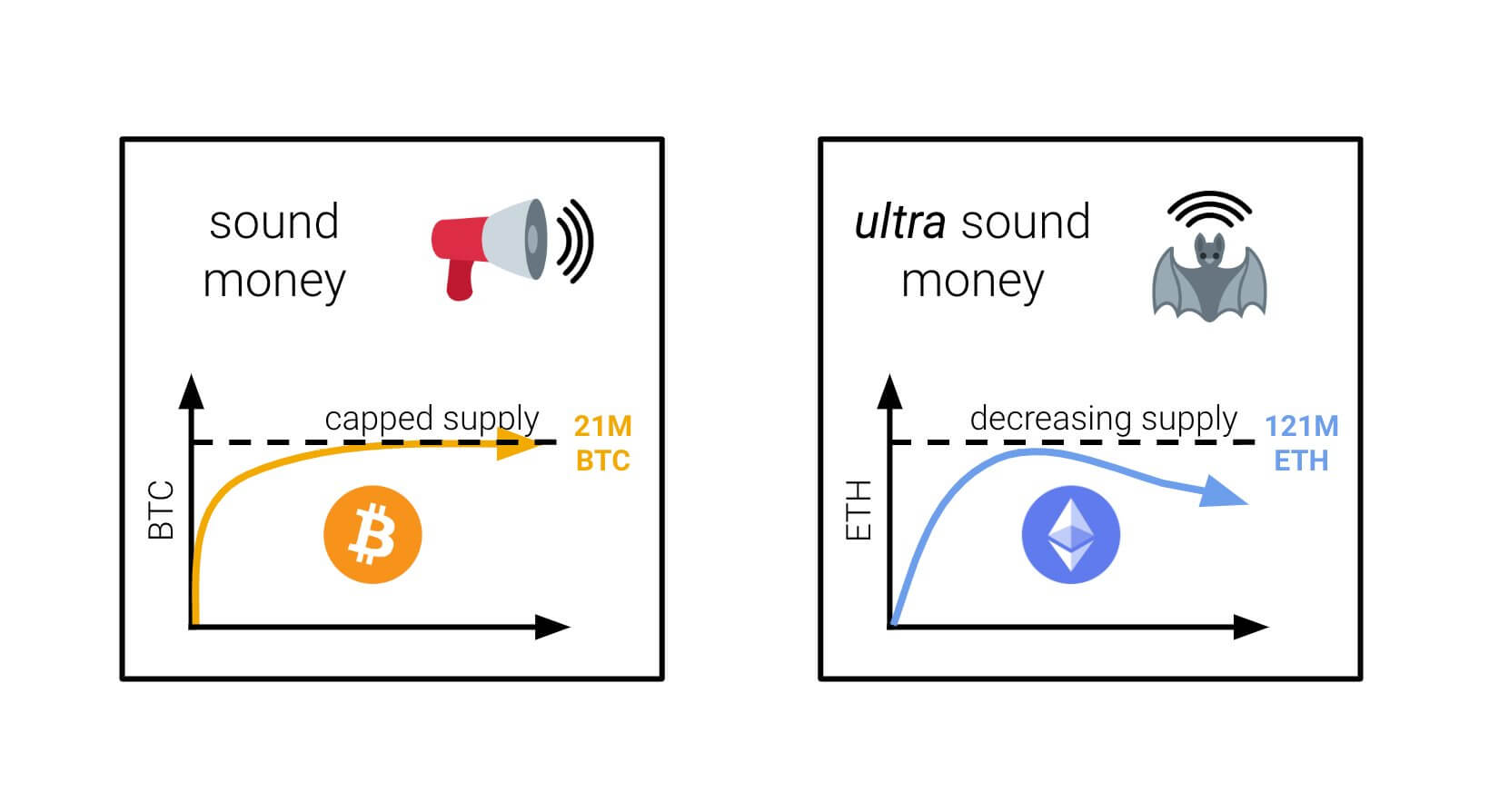
Sound money forms the bedrock of a healthy financial system. It possesses three key attributes:
- Scarcity: A limited supply ensures the coin's value remains stable over time. Bitcoin, with its capped supply of 21 million, is a prime example of sound money.
- Security: A robust and decentralized network safeguards the currency from counterfeiting and manipulation.
- Stability: Sound money exhibits minimal fluctuations in value, making it a dependable store of value.
Ultrasound money builds upon these fundamental properties, introducing an additional dimension: deflation. While sound money maintains a stable or slightly increasing supply, ultrasound money has the potential to become deflationary over time. This means the total supply of the currency could shrink, potentially leading to an increase in its value.
Ethereum's Path to Ultrasound Money
Ethereum, the world's second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, is actively transitioning towards a sound money model and even further, to ultrasound money. This metamorphosis is driven by two key mechanisms:
- Proof-of-Stake (PoS): Ethereum's shift from a proof-of-work (PoW) to a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism significantly reduces the issuance of new coins. In PoW, miners compete to solve complex puzzles to validate transactions and earn rewards. This process is energy-intensive and requires the constant creation of new coins to compensate miners. In PoS, validators stake their existing Ethereum holdings to secure the network and earn rewards. This eliminates the need for energy-guzzling mining and reduces the issuance of new coins.
- EIP-1559: Implemented in August 2021, EIP-1559 introduces a burning mechanism for transaction fees. A portion of the fees paid by users is burned, permanently removing them from circulation. This further reduces the overall supply of Ethereum over time, potentially tipping the scales towards deflation.
For instance, let's imagine a scenario where the amount of Ethereum burned through transaction fees consistently surpasses the issuance of new coins via staking rewards. This would result in a net decrease in the total supply of Ethereum, aligning with the core characteristic of ultrasound money.
Potential Risks and Challenges
The concept of ultrasound money is intriguing, but it's not without its potential drawbacks. Here are a few considerations:
- Hyperinflation: Excessive deflation can be detrimental. If the rate of coin burning outpaces demand, it could lead to a vicious cycle where users hoard the currency in anticipation of further price increases, stifling economic activity.
- Monetary Policy Changes: The trajectory of Ethereum's monetary policy hinges on future protocol upgrades and community decisions. Unforeseen changes could impact the deflationary nature of ultrasound money.
Now you know what these emojis 🦇🔊 mean
The bat and loudspeaker emojis (🦇🔊) have come to symbolize the concept of ultrasound money within the crypto community, representing Ethereum's ambition to transcend the limitations of traditional and digital sound money. These emojis encapsulate the enthusiasm and forward-thinking nature of Ethereum's vision, serving as a shorthand for the transformative potential of Ethereum's economic model post-merge. Through innovations in tokenomics, a deflationary supply mechanism, and a commitment to sustainability and security, Ethereum is on a path to redefine value in the digital age, aiming to become not just a platform for applications but a new standard for money itself.
In conclusion, Ethereum's narrative as ultrasound money is not merely about technological advancements or economic mechanisms; it's about reimagining the foundation of digital value and scarcity. For staking enthusiasts, investors, and the broader crypto community, this narrative offers a vision of a future where money is not just sound but ultrasound, resonating beyond traditional financial boundaries into a new era of blockchain-based finance.
Similar articles.

The Ethereum Merge: Everything You Must Know

The phrase 'Merge' has sparked the imagination of many in the crypto world for quite some time. The Ethereum Merge has been on the minds...

Ankr’s Approach to Safety, Risk, and Protecting Our Community

Ankr Team
November 15, 2022

The crypto and web3 industry has had some dark moments over the past year that have deeply affected communities and, in some cases, have left...

All About Ankr’s Upgraded RPC Platform

Kevin Dwyer
November 24, 2022
Ankr’s new RPC/API platform is upgrading our services offered at app.ankr.com. Learn about new sign-in & payment methods, new features, and how to get started.
Ankr...